Nervous System
The nervous system and muscular system are integrated with one another. Muscles become spastic over time, but symptons can be alleviated. I will now explain how this occurs.
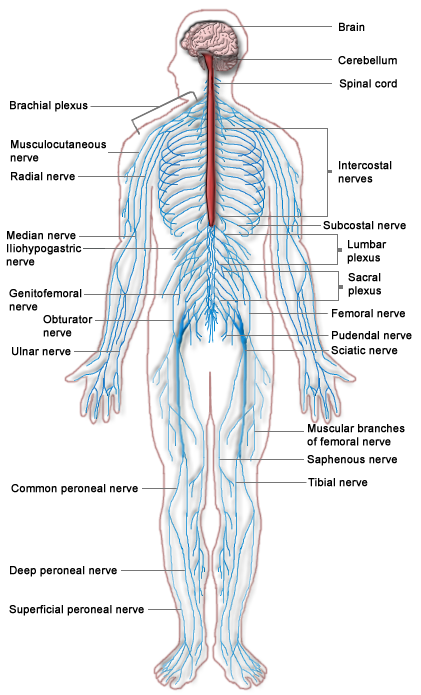
During pregnancy, the central nervous system of the human fetus is the first system to be developed. The central nervous system will then innervate and activate every cell in the body, including the structure of the muscular system.
Muscles work like cables to mobilize the skeletal system (the bones of the human body). Muscles are not independent structures. They receive messages from the central nervous system through reflexes, which are currents of electrical impulses. Reflexes form the communication system between the nervous system and the muscle. These messages inform the muscles to contract, to spasm, or to relax.
When a muscle is painful, it is because the muscle is in a “protective muscle spasm” initiated by the central nervous system. Hyperactivity of the reflex will hold the muscle in spasm. This reflex is indefatigable. It does not get tired and can last for years. In this way, acute pain becomes a chronic condition. Since the spastic muscle is not able to relax, it is held in a constant contraction, resulting in the continuous shortening of muscle fibers.
Muscular System
Muscle fibers then compress and constrict blood vessels, decreasing the ability of the vessels to carry oxygen and nutrition to the muscle cells and to carry away by-products of metabolism (lactic acid). As a result of this process, the chemical environment in the muscle is changed. The muscle will be saturated by lactic acid, which is a noxious irritant for the nervous system and will cause pain. The muscle has become ischemic (oxygen deprived) and spastic.
Joints
Spastic muscles compress the joint (2 or 3 bones attached together), increasing the pressure on the joint during movement. This could affect any joint in the body, including the knee, hip or shoulder. Gradually, the joint itself will deteriorate and may wear out. After many years, it may need to be replaced. Spastic muscles also cause confusion within the central nervous system which can inhibit and weaken other muscles. As the muscular system is thrown out of balance, some muscles will overwork and others may not work at all, resulting in inefficient mobility, excessive energy consumption and pain. Everyday life situations such as long hours sitting at the computer, commuting by car, lack of physical activity, as well as accidental injuries threaten to disrupt muscular balance.
“Muscles are not independent structures. They do not have a mind and cannot on their own decide what to do, to contract, to stretch or to get in spasm.”
Important Facts
Muscle spasms are not a medical condition.
- To provide an effective therapy, first we have to communicate with the nervous system to release the spastic muscles, then to manipulate the muscular and the joints system. The manipulation of muscles and joints will be much more affective in this order
- Muscle spasms are not a medical condition. It is a physical condition of the body and it is being used as a defense mechanism against possible tears or as a reaction to different stresses (physical, emotional, psychological etc.) which might be perceived as a threat to the nervous system. It can become a medical condition because the ability of the muscle spasm to compress blood vessels and compromise blood circulation to the tissues, to entrap nerves and disrupt normal flow of impulses, or to compress joints and damage them. Eventually symptoms will appear.
- A spastic muscle stays contracted because it cannot be lengthened, as a normal healthy one, until the spasm is released.
- Spasm in a muscle can last for years, and will compromise blood circulation, entrap nerves and compress joints.
- The strain counterstrain technique is the most effective technique to release muscle spasm.
- It is counterproductive to either stretch, massage or exercise spastic muscles. These techniques further irritate the nervous system and typically increase pain.s
- Most people have many muscle spasms during their lifetime. They do not know that, unless they touch the muscle and are surprised to find that it is very tender. The cause for this tenderness is that the muscle is saturated with lactic acid. Lactic acid is a noxious irritant for the nervous system which will be perceived as pain by the brain. The muscle will be saturated with lactic acid because the spastic fibers compress the blood vessels, reducing the oxygenation process to the cells and slow down the removal of the lactic acid out of the cells. Once in a while the “low intensity” spasm will change to “high intensity” spasm and the person will “freeze” or as it is more commonly expressed, “my back or my neck went out”.
- Muscles are not independent structures. They do not have a mind and cannot on their own decide what to do, to contract, to stretch or to get in spasm. Since they carry sensors and receptors they constantly get signals (nerve impulses-reflex) and receive signals from the central nervous system and respond to this information. So when you feel pain in the muscle because it is in spasm, do not blame the muscle for that. The cause of the spasm is in the spasm reflex mechanism which is triggered by the nervous system!
- Joints (2 or 3 bones attached to each other) cannot move on their own. They are pulled by muscles.
- Joints cannot stay where they belong after being manipulated if the muscles which surround them are still tight and spastic.
- The foundation of the body is in the hips because the body’s gravity center is there. We have a “righting reflex,” which means that we need to keep the eyes leveled horizontally all the time. If they are not leveled, we get dizzy and unable to function. All muscle activity between the hips and the eyes is just the attempt of the nervous system to keep the eyes leveled according to the position of the hips.